

In a similar vein, Pāṇini (5th century BC) used the null (zero) operator in the Ashtadhyayi, an early example of an algebraic grammar for the Sanskrit language (also see Pingala).
In mathematics texts this word often refers to the number zero. Indian texts used a Sanskrit word Shunye or shunya to refer to the concept of void. Egyptians used the word nfr to denote zero balance in double entry accounting. The use of 0 as a number should be distinguished from its use as a placeholder numeral in place-value systems.
ARE ALL NUMBERS REAL NUMBERS PLUS
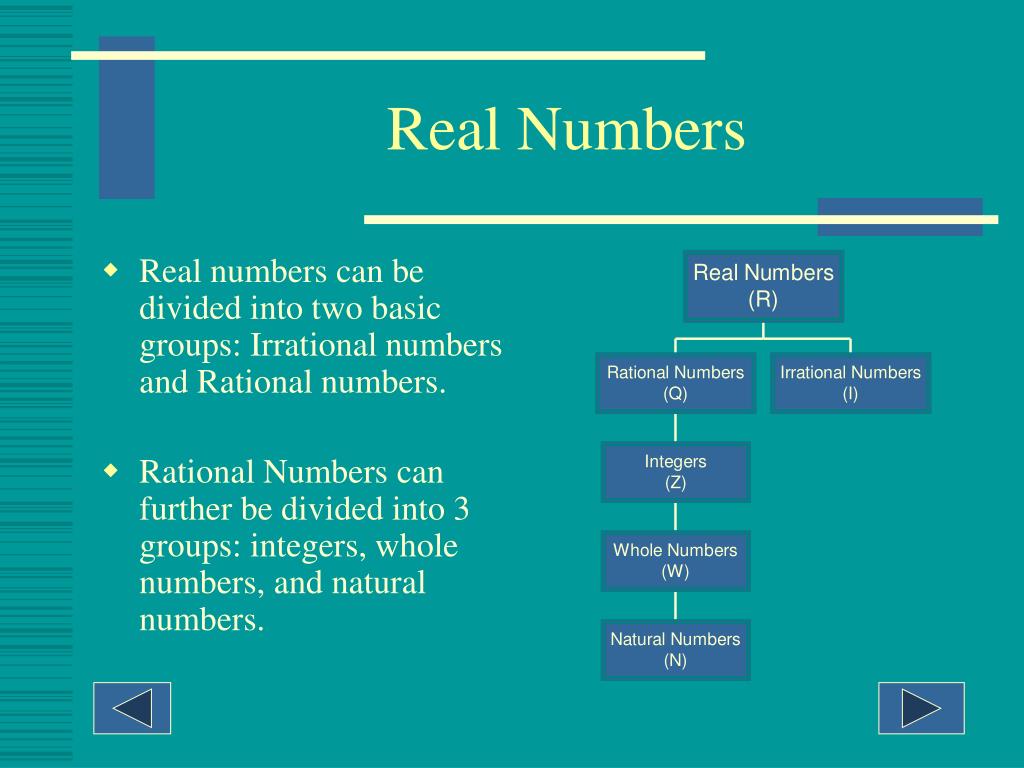
He gave rules of using zero with negative and positive numbers, such as "zero plus a positive number is a positive number, and a negative number plus zero is the negative number." The Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta is the earliest known text to treat zero as a number in its own right, rather than as simply a placeholder digit in representing another number as was done by the Babylonians or as a symbol for a lack of quantity as was done by Ptolemy and the Romans. Early use of zero as a decimal figure.īrahmagupta's Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta is the first book that mentions zero as a number, hence Brahmagupta is usually considered the first to formulate the concept of zero. The number 605 in Khmer numerals, from an inscription from 683 AD. By this time (the 7th century) the concept had clearly reached Cambodia as Khmer numerals, and documentation shows the idea later spreading to China and the Islamic world. He treated 0 as a number and discussed operations involving it, including division. The first known documented use of zero dates to AD 628, and appeared in the Brāhmasphuṭasiddhānta, the main work of the Indian mathematician Brahmagupta. ( November 2022) ( Learn how and when to remove this template message) Unsourced material may be challenged and removed. Please help improve this article by adding citations to reliable sources in this section. This section needs additional citations for verification. In modern mathematics, number systems are considered important special examples of more general algebraic structures such as rings and fields, and the application of the term "number" is a matter of convention, without fundamental significance. Among the first were the hypercomplex numbers, which consist of various extensions or modifications of the complex number system. ĭuring the 19th century, mathematicians began to develop many different abstractions which share certain properties of numbers, and may be seen as extending the concept. Numerology heavily influenced the development of Greek mathematics, stimulating the investigation of many problems in number theory which are still of interest today. Though it is now regarded as pseudoscience, belief in a mystical significance of numbers, known as numerology, permeated ancient and medieval thought. For example, in Western society, the number 13 is often regarded as unlucky, and " a million" may signify "a lot" rather than an exact quantity. Their study or usage is called arithmetic, a term which may also refer to number theory, the study of the properties of numbers.īesides their practical uses, numbers have cultural significance throughout the world. Calculations with numbers are done with arithmetical operations, the most familiar being addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, and exponentiation. In mathematics, the notion of number has been extended over the centuries to include zero (0), negative numbers, rational numbers such as one half ( 1 2 ) and π, and complex numbers which extend the real numbers with a square root of −1 (and its combinations with real numbers by adding or subtracting its multiples). In common usage, a numeral is not clearly distinguished from the number that it represents.
ARE ALL NUMBERS REAL NUMBERS SERIAL
In addition to their use in counting and measuring, numerals are often used for labels (as with telephone numbers), for ordering (as with serial numbers), and for codes (as with ISBNs). The most common numeral system is the Hindu–Arabic numeral system, which allows for the representation of any number using a combination of ten fundamental numeric symbols, called digits. As only a relatively small number of symbols can be memorized, basic numerals are commonly organized in a numeral system, which is an organized way to represent any number.

More universally, individual numbers can be represented by symbols, called numerals for example, "5" is a numeral that represents the number five. Numbers can be represented in language with number words. The original examples are the natural numbers 1, 2, 3, 4, and so forth. For other uses, see Number (disambiguation).Ī number is a mathematical object used to count, measure, and label.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
